Map:35e3nrg5ox0= Mt Vesuvius
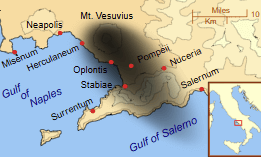
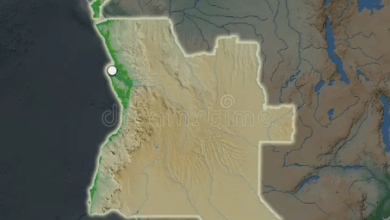
The map designated as 35e3nrg5ox0 provides a comprehensive overview of Mt. Vesuvius, a stratovolcano with a complex history marked by both catastrophic eruptions and a vibrant ecosystem. Notably, the infamous eruption of 79 AD serves as a pivotal moment in history, forever altering the landscape and the lives of those in nearby Pompeii and Herculaneum. However, the geological features of Vesuvius extend beyond its historical narrative, raising critical questions about the ongoing risks it poses today. What implications do these factors have for the local communities and their future?
Overview of Mt. Vesuvius
Mount Vesuvius, a stratovolcano located in Campania, Italy, is one of the most studied and closely monitored volcanoes in the world due to its history of explosive eruptions and its proximity to densely populated areas.
Its volcanic activity not only poses significant risks but also holds immense cultural significance, influencing local traditions, art, and historical narratives, thereby shaping the identity of surrounding communities.
See also: Map:15crfwomb6q= Puerto Vallarta
Historical Eruptions and Impact
Throughout its history, Vesuvius has erupted over 50 times, with several significant eruptions shaping both the geological landscape and the sociocultural fabric of the region.
The eruption of 79 AD, which buried the Pompeii ruins, serves as a pivotal moment in the eruption timeline, illustrating the devastating consequences of volcanic activity.
Such events have profoundly influenced urban development and disaster preparedness in surrounding areas.
Geological Features and Research
The geological features of Mt. Vesuvius are characterized by its stratovolcano structure, resulting from diverse volcanic activity over millennia.
Research indicates that its magma composition is primarily andesitic, contributing to explosive eruptions.
This distinct composition influences eruption dynamics and hazard assessment, making ongoing geological studies crucial for understanding the volcano’s behavior and potential impact on surrounding populations and environments.
The Surrounding Environment
Situated in a densely populated region of southern Italy, Mt. Vesuvius influences the surrounding environment significantly.
The area boasts remarkable flora diversity, featuring endemic species adapted to volcanic soils. Additionally, it serves as vital wildlife habitats, supporting various fauna.
The interplay between human activity and natural ecosystems highlights the delicate balance necessary for preserving these unique ecological zones while promoting sustainable coexistence with the surrounding communities.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Mt. Vesuvius remains a significant geological and cultural landmark, with its most notorious eruption in 79 AD resulting in the preservation of Pompeii and Herculaneum beneath volcanic ash. Remarkably, the volcano has erupted over 50 times since its formation, emphasizing its ongoing threat to the densely populated areas surrounding it. Understanding the geological features and historical context of Vesuvius is crucial for assessing volcanic risks and implementing effective disaster preparedness strategies in the region.